2 月 . 14, 2025 02:39
Back to list
معدات التغويز
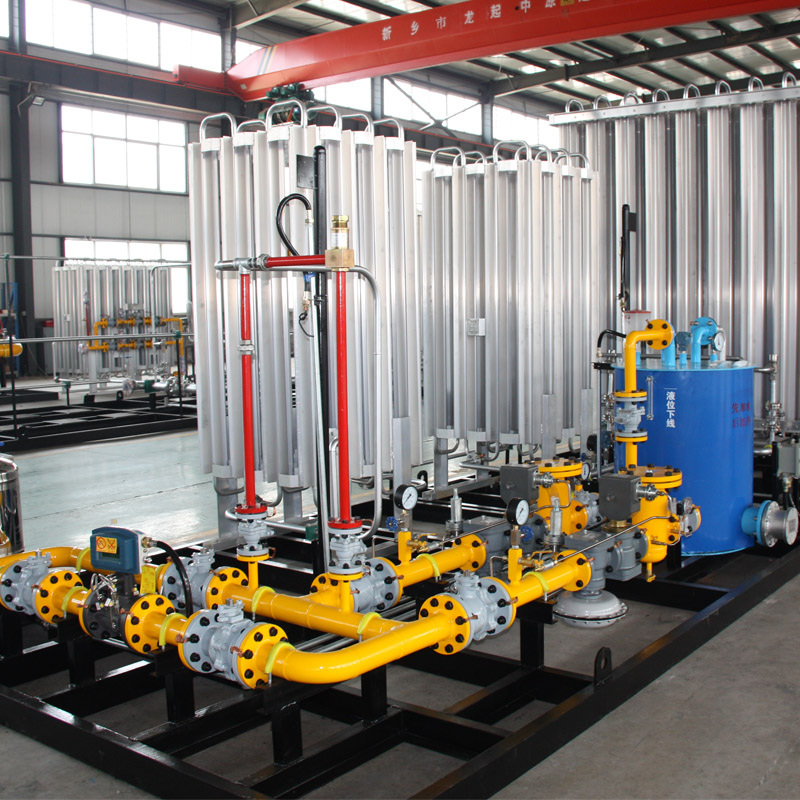
Gasification equipment plays a crucial role in the transformation of carbon-based materials into synthetic gas, a cleaner energy alternative. In today's world where sustainable and renewable energy solutions gain ever-increasing importance, understanding the essentials of gasification technology, its applications, and its benefits becomes imperative.
Real-world applications have proven the robust potential of gasification technology. In industrial sectors, gasification not only contributes to power generation but also fosters the growth of synthetic fuel production, which can power vehicles, reducing dependency on conventional fuels. In developing regions, small-scale gasification units have enabled local communities to generate energy from agricultural waste, fostering energy independence and promoting sustainable practices. Trustworthiness and reliability of gasification equipment are paramount. Manufacturers focus on delivering systems that meet stringent industry standards and certifications. Companies investing in gasification systems are advised to prioritize well-established brands with significant experience and a track record in the industry. This ensures that the equipment not only meets current needs but is adaptable to future demands. Proper maintenance and operation, guided by experienced personnel, further safeguard the efficiency and longevity of gasification systems. Continuous monitoring technologies and automated controls are embedded in modern equipment designs to ensure seamless operation and early detection of potential issues. The synergy between technical expertise and innovative design has enabled gasification equipment to emerge as a game changer in transitioning towards a low-carbon economy. Its ability to convert diverse feedstocks into valuable and cleaner energy forms underscores its role in addressing global energy challenges. As technology continues to advance, further innovations within gasification systems are expected, promising greater efficiencies and broader applications across industries. In conclusion, the nuanced understanding of gasification equipment's design, functioning, and application reflects not only a technical marvel but also a strategic approach to environmental sustainability. As businesses, governments, and communities look towards cleaner energy solutions, gasification stands out as a viable and increasingly attractive option. Its proven benefits in energy production, waste management, and emissions reduction highlight its critical role in shaping the future of energy and resource management.
Real-world applications have proven the robust potential of gasification technology. In industrial sectors, gasification not only contributes to power generation but also fosters the growth of synthetic fuel production, which can power vehicles, reducing dependency on conventional fuels. In developing regions, small-scale gasification units have enabled local communities to generate energy from agricultural waste, fostering energy independence and promoting sustainable practices. Trustworthiness and reliability of gasification equipment are paramount. Manufacturers focus on delivering systems that meet stringent industry standards and certifications. Companies investing in gasification systems are advised to prioritize well-established brands with significant experience and a track record in the industry. This ensures that the equipment not only meets current needs but is adaptable to future demands. Proper maintenance and operation, guided by experienced personnel, further safeguard the efficiency and longevity of gasification systems. Continuous monitoring technologies and automated controls are embedded in modern equipment designs to ensure seamless operation and early detection of potential issues. The synergy between technical expertise and innovative design has enabled gasification equipment to emerge as a game changer in transitioning towards a low-carbon economy. Its ability to convert diverse feedstocks into valuable and cleaner energy forms underscores its role in addressing global energy challenges. As technology continues to advance, further innovations within gasification systems are expected, promising greater efficiencies and broader applications across industries. In conclusion, the nuanced understanding of gasification equipment's design, functioning, and application reflects not only a technical marvel but also a strategic approach to environmental sustainability. As businesses, governments, and communities look towards cleaner energy solutions, gasification stands out as a viable and increasingly attractive option. Its proven benefits in energy production, waste management, and emissions reduction highlight its critical role in shaping the future of energy and resource management.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024


