
2 月 . 20, 2025 07:54
Back to list
صمام هوائي
Pneumatic valves, or صمام هوائي in Arabic, play an integral role in various industrial applications, ensuring fluid control and automation. Selecting the ideal pneumatic valve for specific operations can significantly enhance productivity and safety, crucial for industries like manufacturing, automotive, chemical processing, and more. Understanding the intricacies of these components is vital for engineers and technical professionals seeking to implement efficient control systems.
Selecting the right pneumatic valve involves assessing several critical factors. A comprehensive understanding of system requirements, operating conditions, and specific application needs is essential. The size and type of valve chosen can impact not just the functionality but also the efficiency of the system. Variables such as the operating pressure range, temperature conditions, and the nature of the gas being controlled are pivotal in making the right choice. The expertise of a reliable pneumatic valve manufacturer or supplier is invaluable, often providing guidance to ensure the appropriate selection and application. They offer a breadth of knowledge, including custom solutions where standard options don't suffice. Their experience can greatly enhance a technical professional's ability to implement optimal, sustainable systems. Additionally, maintenance plays a crucial role in the longevity and reliability of pneumatic systems. Routine checks for possible leaks, wear and tear, and performance issues ensure that the valves perform optimally over time. Proper lubrication, timely replacements, and a proactive approach to system maintenance can prevent downtime and enhance efficiency. Given the global shift toward automation and the increasing demand for efficient control systems, pneumatic valves have become indispensable in modern industry. Their contribution to energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced safety standards is pivotal, underscoring the value they bring to industrial processes. In conclusion, pneumatic valves are a critical component of pneumatic systems, offering various functionalities to meet the diverse needs of industrial applications. Their versatility, combined with expert insights from manufacturers and regular maintenance, ensures their role as a cornerstone of efficiency, reliability, and safety in industrial operations. Companies investing in high-quality pneumatic solutions not only boost their operational capabilities but also position themselves strategically for future advancements in automation and control technology.
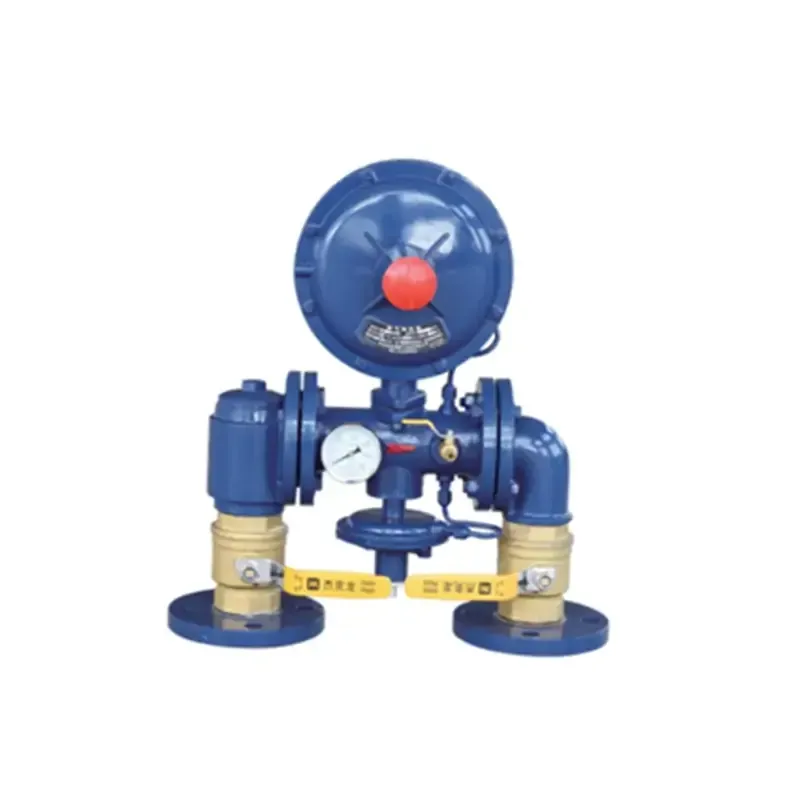
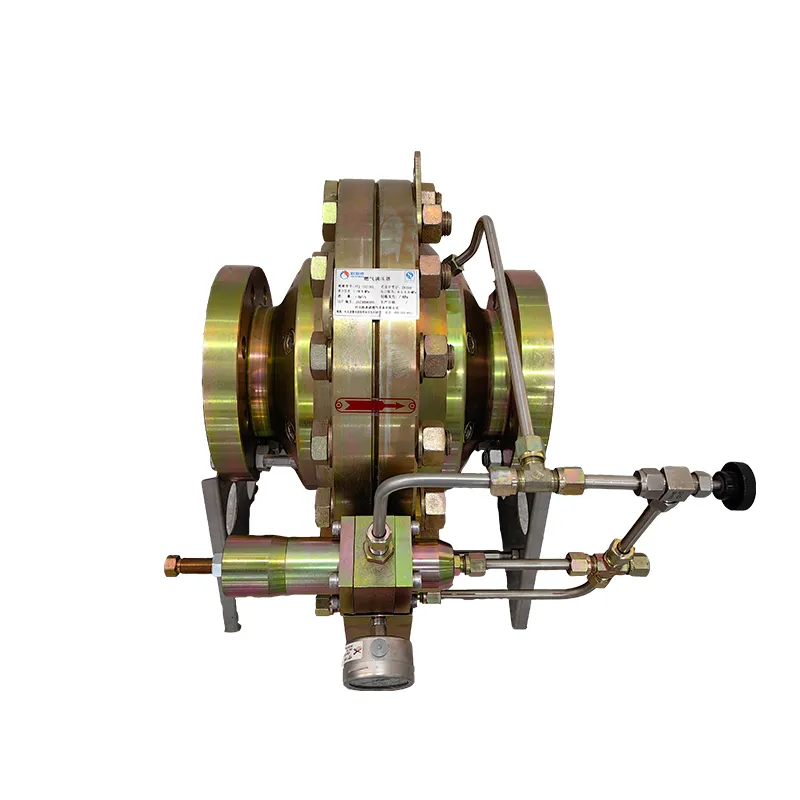

Selecting the right pneumatic valve involves assessing several critical factors. A comprehensive understanding of system requirements, operating conditions, and specific application needs is essential. The size and type of valve chosen can impact not just the functionality but also the efficiency of the system. Variables such as the operating pressure range, temperature conditions, and the nature of the gas being controlled are pivotal in making the right choice. The expertise of a reliable pneumatic valve manufacturer or supplier is invaluable, often providing guidance to ensure the appropriate selection and application. They offer a breadth of knowledge, including custom solutions where standard options don't suffice. Their experience can greatly enhance a technical professional's ability to implement optimal, sustainable systems. Additionally, maintenance plays a crucial role in the longevity and reliability of pneumatic systems. Routine checks for possible leaks, wear and tear, and performance issues ensure that the valves perform optimally over time. Proper lubrication, timely replacements, and a proactive approach to system maintenance can prevent downtime and enhance efficiency. Given the global shift toward automation and the increasing demand for efficient control systems, pneumatic valves have become indispensable in modern industry. Their contribution to energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced safety standards is pivotal, underscoring the value they bring to industrial processes. In conclusion, pneumatic valves are a critical component of pneumatic systems, offering various functionalities to meet the diverse needs of industrial applications. Their versatility, combined with expert insights from manufacturers and regular maintenance, ensures their role as a cornerstone of efficiency, reliability, and safety in industrial operations. Companies investing in high-quality pneumatic solutions not only boost their operational capabilities but also position themselves strategically for future advancements in automation and control technology.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

