
2 月 . 20, 2025 10:59
Back to list
RTJ2-*/*HL series gas pressure regulator
Pressure reducers, known in Arabic as مخفض الضغط, are vital components in various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of systems requiring pressure regulation. These devices maintain a desired output pressure regardless of fluctuations in input pressure, offering stability and safety. Delving into the intricacies of pressure reducers reveals their critical value across multiple applications, including in medical, industrial, and domestic settings.
Trustworthiness in pressure reducers can be augmented by understanding their maintenance needs and lifecycle management. Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of worn-out parts are pivotal in upholding their functionality. For instance, leading companies in the manufacturing of pressure reducers recommend biannual maintenance checks and offer service programs that include real-time monitoring with IoT integrations. This not only enhances reliability but also enables predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions. In the medical field, pressure reducers play a crucial role in gas delivery systems. Oxygen tanks, for example, depend heavily on these devices to ensure patients receive the correct flow rate and pressure of oxygen. In emergency medical services (EMS), the precision of pressure reducers can significantly influence patient outcomes, where the slightest miscalculation in pressure can lead to inadequate ventilation or damage to lung tissue. Certified medical professionals rely on pressure reducers that have undergone rigorous testing and validation, illuminating the life-saving potential embedded within their operational precision. Domestic applications of pressure reducers further solidify their everyday importance. These include residential water systems where pressure variance can lead to pipe damage or water wastage. By maintaining consistent water pressure, these devices help households conserve water while preventing unexpected appliance breakdowns. Reports from a municipal water management study revealed that neighborhoods implementing home water pressure reducers saw a reduction in water usage by up to 25%, translating to both economic savings for homeowners and ecological benefits for the community. In conclusion, pressure reducers are indispensable for maintaining system stability across various sectors. With real-world applications ranging from industrial safety enhancements to medical precision and domestic utility management, they embody an essential component in pressure-sensitive operations. Their selection, installation, and maintenance require considerable expertise, and adherence to authoritative standards strengthens their dependability. As innovations in this field continue to emerge, the role of pressure reducers is poised to expand, offering increasingly smarter solutions that enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability.
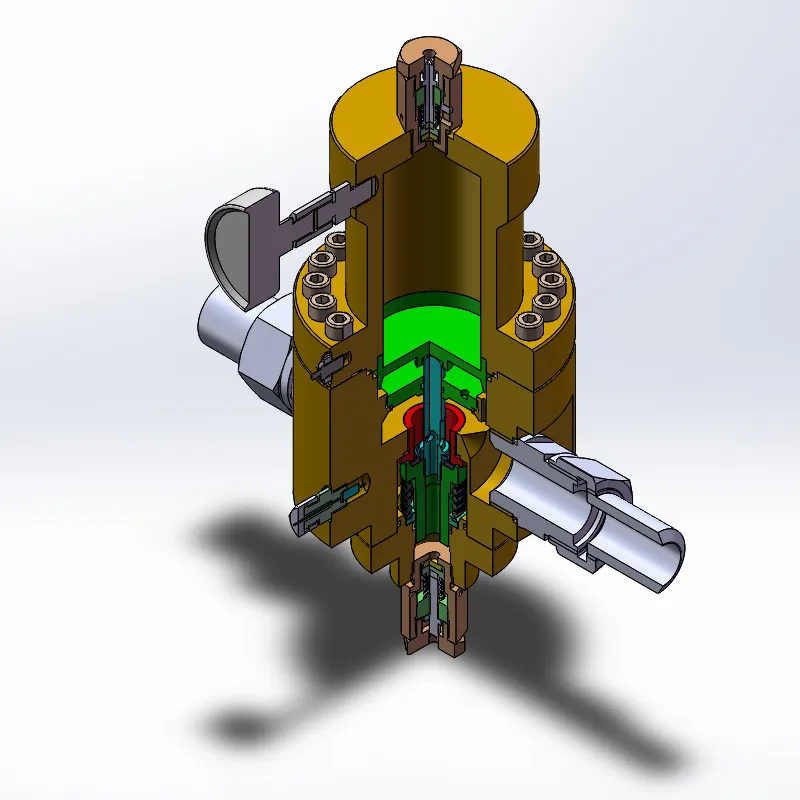
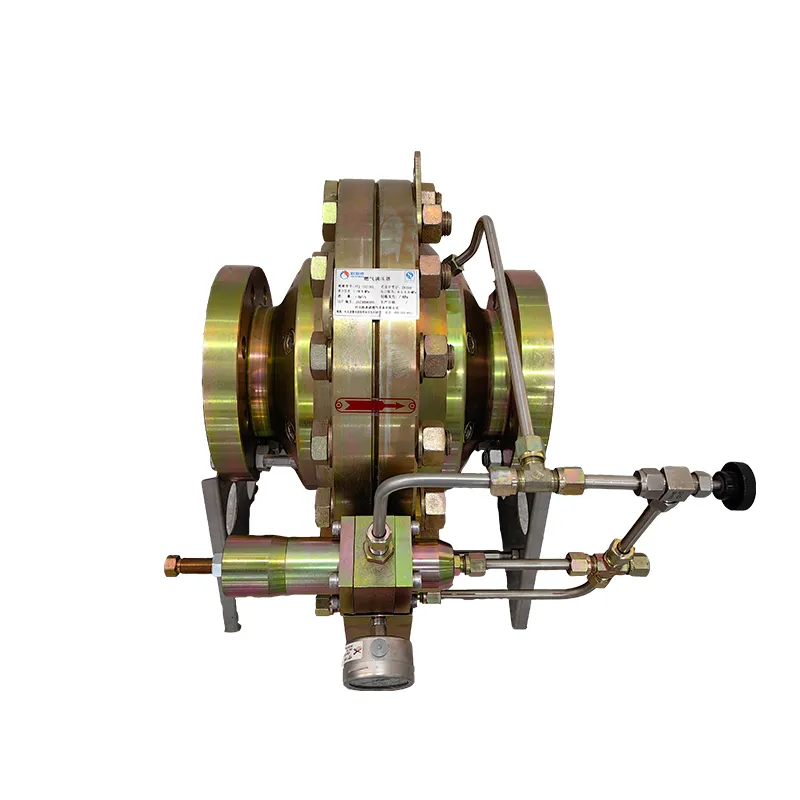
Trustworthiness in pressure reducers can be augmented by understanding their maintenance needs and lifecycle management. Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of worn-out parts are pivotal in upholding their functionality. For instance, leading companies in the manufacturing of pressure reducers recommend biannual maintenance checks and offer service programs that include real-time monitoring with IoT integrations. This not only enhances reliability but also enables predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions. In the medical field, pressure reducers play a crucial role in gas delivery systems. Oxygen tanks, for example, depend heavily on these devices to ensure patients receive the correct flow rate and pressure of oxygen. In emergency medical services (EMS), the precision of pressure reducers can significantly influence patient outcomes, where the slightest miscalculation in pressure can lead to inadequate ventilation or damage to lung tissue. Certified medical professionals rely on pressure reducers that have undergone rigorous testing and validation, illuminating the life-saving potential embedded within their operational precision. Domestic applications of pressure reducers further solidify their everyday importance. These include residential water systems where pressure variance can lead to pipe damage or water wastage. By maintaining consistent water pressure, these devices help households conserve water while preventing unexpected appliance breakdowns. Reports from a municipal water management study revealed that neighborhoods implementing home water pressure reducers saw a reduction in water usage by up to 25%, translating to both economic savings for homeowners and ecological benefits for the community. In conclusion, pressure reducers are indispensable for maintaining system stability across various sectors. With real-world applications ranging from industrial safety enhancements to medical precision and domestic utility management, they embody an essential component in pressure-sensitive operations. Their selection, installation, and maintenance require considerable expertise, and adherence to authoritative standards strengthens their dependability. As innovations in this field continue to emerge, the role of pressure reducers is poised to expand, offering increasingly smarter solutions that enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability.
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

