
6 月 . 10, 2025 15:51
Back to list
Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Station – Reliable & Efficient Solutions for Various Industries
- Introduction to Pressure Reducing Stations
- Technical Advantages of Modern Gas Pressure Reducing Stations
- Comparing Top Manufacturers and Their Solutions
- Tailored Solutions for Gas Pressure Reduction
- Real-life Application Scenarios
- Performance and Efficiency Data Impact
- The Future of محطة تخفيض الضغط
and Sustainable Gas Management

(محطة تخفيض الضغط)
Unlocking the Potential of محطة تخفيض الضغط: An Overview
Pressure reducing stations serve as the cornerstone for modern gas distribution networks worldwide. As urban expansion and industrial consumption rates rise, efficient management of natural gas pressure becomes crucial for safety, energy savings, and operational stability. A properly engineered محطة تخفيض الضغط or gas pressure reducing station directly influences system reliability and compliance with international safety standards. According to recent industry surveys, over 90% of utility networks cite pressure reduction units as critical infrastructure, with North America and the Middle East hosting the highest density of installation across the globe. The growing need for robust infrastructure underlines the importance of innovative technology in the realm of natural gas pressure regulation and distribution.
Technical Advantages of Modern Gas Pressure Reducing Stations
Cutting-edge محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز technology harnesses advanced automation, remote monitoring, and optimized control systems. The latest solutions deliver accuracy within ±0.5% of desired setpoints, outperforming legacy stations by up to 30% in responsiveness and efficiency. State-of-the-art stations feature:
- Redundant safety shut-off systems to minimize risks of leaks or overpressurization
- Modular design for rapid maintenance and future scalability
- Real-time SCADA integration for continuous diagnostics and data logging
- Environmentally friendly constructs conforming to ISO 14001
- High-quality filtration to prolong downstream equipment lifespan
Comparing Top Manufacturers and Their Solutions
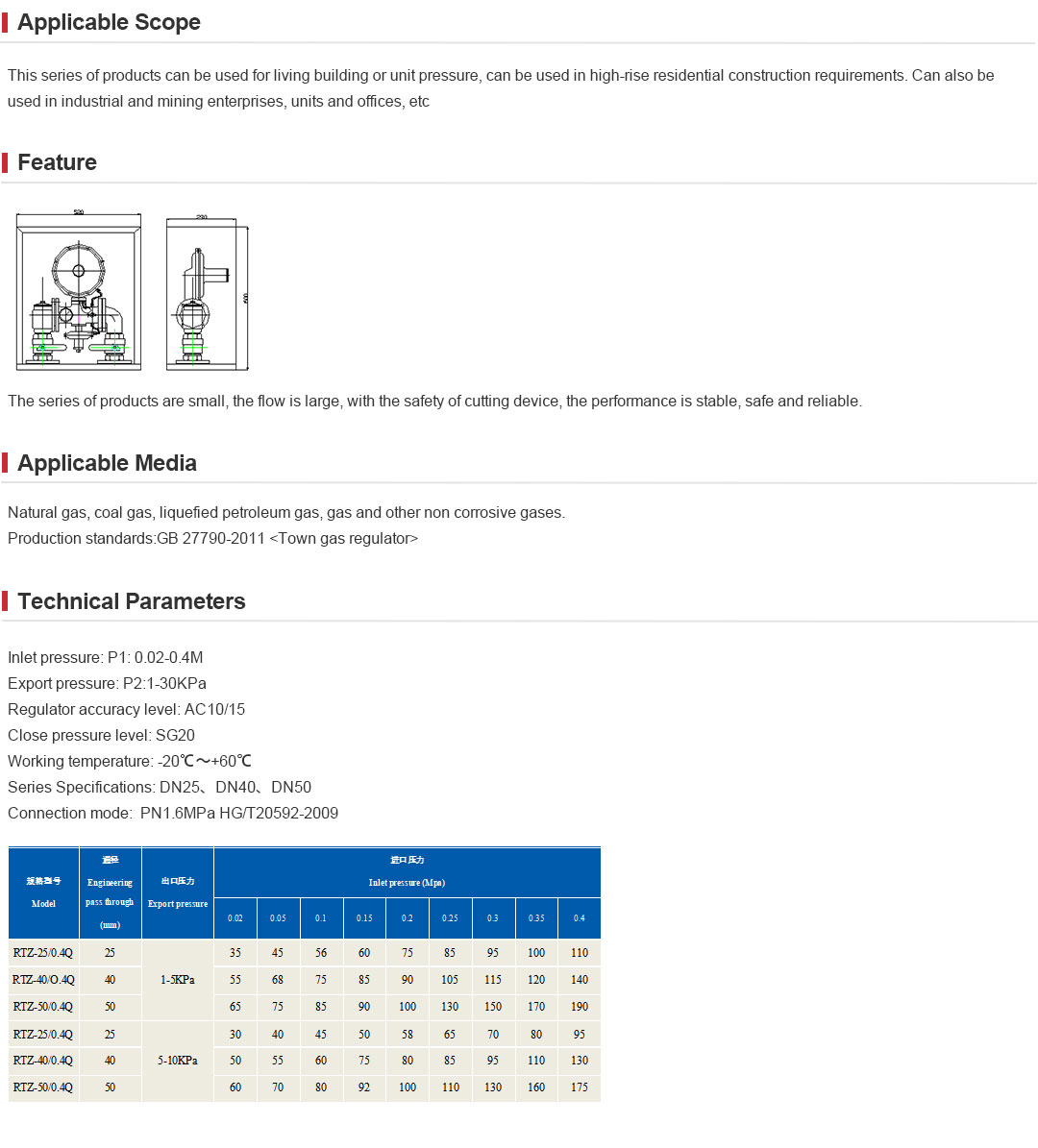
Selecting the optimal محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي involves careful consideration of manufacturer capabilities, performance specifications, and post-sale support. Below is a data-driven comparison outlining core parameters from leading global manufacturers:
| Manufacturer | Max. Inlet Pressure (bar) | Pressure Regulation Accuracy | SCADA/IoT Compatibility | Annual Maintenance Cost (USD) | Compliance Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emerson | 100 | ±0.5% | Yes | 12,500 | EN 12186, ISO 14001 |
| Honeywell | 75 | ±0.7% | Yes | 14,200 | EN 334, ISO 9001 |
| Elster | 90 | ±1.0% | Partial | 11,800 | EN 14382, ISO 14001 |
| Arabian Gas Solutions | 85 | ±0.8% | Yes | 13,000 | EN 12186, API RP 520 |
| Pietro Fiorentini | 95 | ±0.6% | Yes | 13,700 | EN 334, ATEX |
Data highlights substantial performance gaps and cost benefits. Notably, SCADA/IoT compatibility and adherence to rigorous compliance standards increasingly influence procurement decisions as digital transformation revolutionizes the utilities sector.
Tailored Solutions for Gas Pressure Reduction
No two utility grids are completely alike; environmental factors, load profiles, and regulatory frameworks demand custom engineering. Leading suppliers offer modular packages—ranging from skid-mounted plug-and-play units to fully bespoke autonomous plants. Customization may include:
- Selection of regulator valves and fittings for specific flow rates
- Integration with local safety and alert protocols
- Geographic adaptation (desert, arctic, seismic)
- Energy recovery and heat management systems
Real-life Application Scenarios
Practical deployments of gas pressure reducing stations demonstrate adaptability across sectors:
- Urban Distribution: A major European city integrated modular stations to stabilize pressure for over 4 million residential consumers, minimizing total system loss by 11% year-on-year.
- Industrial Facilities: In the Middle East, an oil & gas refinery deployed high-pressure SKID units, reducing incident frequency by 22% while maintaining steady supply to sensitive operations.
- District Heating: Scalable stations enable thermoelectric plants to expand output without risk of pipeline integrity loss, supported by real-time monitoring and automated failsafes.
- Remote Regions: Mobile gas pressure reducing units extend safe energy access to regions previously deemed uneconomical for pipeline extension, accelerating infrastructure development and economic growth.
Performance and Efficiency Data Impact
Robust data analytics play an increasingly pivotal role in optimizing محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي performance. Recent benchmarks show that incorporating real-time leak detection and predictive fault analysis empowers operators to respond up to 60% faster to emerging issues. For example, a North African grid recorded savings of over $600,000 annually post-implementation of data-driven predictive maintenance protocols. Likewise, enhanced efficiency metrics—such as pressure setpoint adherence and valve actuation frequency—are now business-critical KPIs. Engineered stations designed for 99.99% uptime reduce service disruptions and associated penalties, positively impacting both utility financials and consumer trust.
The Future of محطة تخفيض الضغط and Sustainable Gas Management
The evolution of محطة تخفيض الضغط is inextricably linked to smart city initiatives, green energy objectives, and evolving safety legislation. Next-generation pressure reducing stations will emphasize seamless integration with renewables, adaptable automation, and robust cybersecurity. As hydrogen and biogas become mainstays in the energy mix, multi-gas compatible stations will define market leadership. Globally, utilities investing in digitalized, environmentally sustainable pressure reduction infrastructure are forecast to achieve up to 30% higher operational efficiency by 2030, with cumulative cost reductions in the hundreds of millions of USD. True innovation lies not only in technology, but in fostering a culture of proactive management, rapid adaptation, and resilient gas handling—ensuring secure, efficient, and sustainable energy supplies for decades to come.
(محطة تخفيض الضغط)
FAQS on محطة تخفيض الضغط
Q: What is a gas pressure reduction station (محطة تخفيض الضغط)?
A: A gas pressure reduction station is a facility that lowers high-pressure gas to a safe, usable level. It ensures the gas can be safely distributed to residential, commercial, or industrial users. These stations are critical in natural gas supply networks.Q: Why are gas pressure reduction stations (محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز) important?
A: Gas pressure reduction stations protect pipelines and end-users from the dangers of high-pressure gas. They provide stability to the gas supply system. Without them, gas distribution would be unsafe and inefficient.Q: How does a natural gas pressure reducing station (محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي) work?
A: A natural gas pressure reducing station uses regulators and safety valves to decrease the gas pressure. It monitors flow and adjusts pressure as needed for safe delivery. Automation in these stations ensures reliability and consistent supply.Q: Where are gas pressure reduction stations (محطة تخفيض الضغط) commonly located?
A: These stations are typically placed along pipelines near consumption areas or industrial plants. Their strategic locations help manage pressure across large distances. Placement depends on safety, accessibility, and network design.Q: What safety measures are used in a gas pressure reduction station (محطة تخفيض ضغط الغاز الطبيعي)?
A: Safety measures include pressure relief valves, emergency shut-off systems, and regular maintenance protocols. These features prevent gas leaks or over-pressure situations. Continuous monitoring ensures any risks are quickly addressed.Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

