
3 月 . 07, 2025 04:25
Back to list
lng
Exploring the realm of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) offers a fascinating glimpse into a product that has become increasingly vital to the global energy market. As an expert in this field, I can provide a detailed analysis that delves into the multifaceted applications and implications of LNG, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of its importance and effectiveness.
LNG's economic implications cannot be overlooked. The presence of LNG infrastructure such as liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, and carrier fleets generates significant economic activity. New projects often mean job creation, both in construction and ongoing operational roles, contributing to economic growth in regions hosting these facilities. Furthermore, countries with substantial natural gas reserves see significant revenue from LNG exports, which can fund domestic development projects or strengthen national economies. However, the focus on LNG should not obscure the challenges it presents. Understanding its entire lifecycle, from extraction to liquefaction, transportation, and eventual usage, calls for rigorous attention to safety protocols and environmental protection. The industry must address issues such as methane leakage, a potent greenhouse gas, during extraction and transportation phases. Thus, investment in research improving efficiency and reducing emissions at every stage is crucial, underscoring the need for authoritative solutions that balance energy demands with environmental responsibilities. Trustworthiness in the LNG market is embedded in regulation and transparency. Governing bodies and industry standards play a critical role in maintaining high levels of safety and environmental stewardship. From stringent maritime standards for LNG carriers to local and international regulations governing the entire value chain, adherence to these established benchmarks ensures reliability and safety, both paramount to maintaining public trust in LNG as a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure. Enlightening the public about LNG's role in energy systems forms an integral part of building trust and understanding. Comprehensive educational efforts at every level, particularly in communities near LNG facilities, forge a rapport between energy providers and consumers. These initiatives emphasize transparency, safety, and environmental commitment, laying a foundation of trust that supports both the public perception and practical realization of LNG projects. In conclusion, LNG represents a highly strategic, economic, and environmental asset in the global push towards more flexible, secure, and sustainable energy systems. Expert insights demonstrate that when managed prudently, LNG stands as an exemplar of modern energy solutions, promising a brighter, cleaner, and more connected energy future.
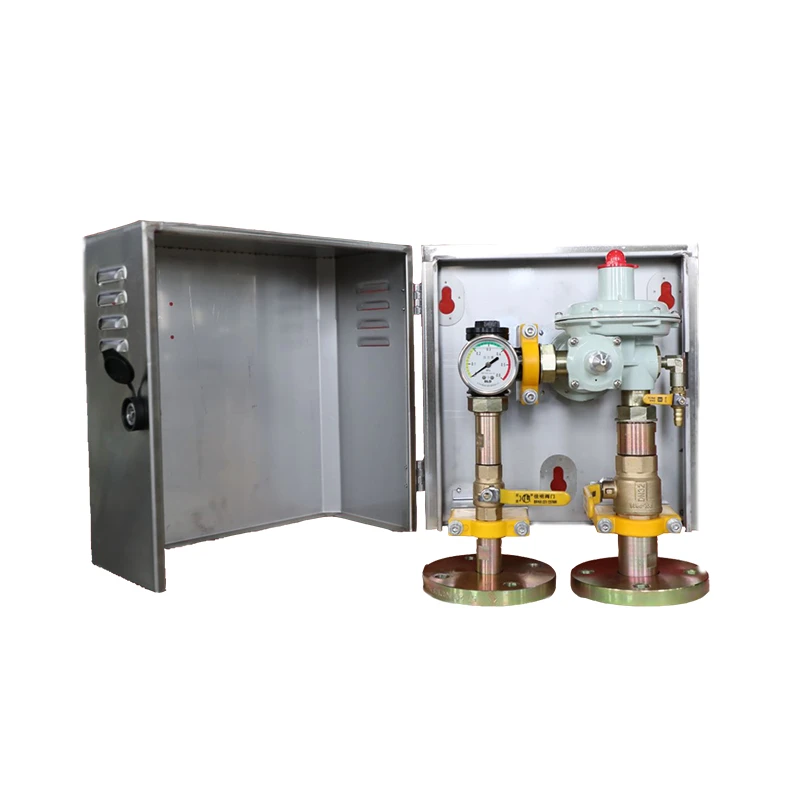

LNG's economic implications cannot be overlooked. The presence of LNG infrastructure such as liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, and carrier fleets generates significant economic activity. New projects often mean job creation, both in construction and ongoing operational roles, contributing to economic growth in regions hosting these facilities. Furthermore, countries with substantial natural gas reserves see significant revenue from LNG exports, which can fund domestic development projects or strengthen national economies. However, the focus on LNG should not obscure the challenges it presents. Understanding its entire lifecycle, from extraction to liquefaction, transportation, and eventual usage, calls for rigorous attention to safety protocols and environmental protection. The industry must address issues such as methane leakage, a potent greenhouse gas, during extraction and transportation phases. Thus, investment in research improving efficiency and reducing emissions at every stage is crucial, underscoring the need for authoritative solutions that balance energy demands with environmental responsibilities. Trustworthiness in the LNG market is embedded in regulation and transparency. Governing bodies and industry standards play a critical role in maintaining high levels of safety and environmental stewardship. From stringent maritime standards for LNG carriers to local and international regulations governing the entire value chain, adherence to these established benchmarks ensures reliability and safety, both paramount to maintaining public trust in LNG as a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure. Enlightening the public about LNG's role in energy systems forms an integral part of building trust and understanding. Comprehensive educational efforts at every level, particularly in communities near LNG facilities, forge a rapport between energy providers and consumers. These initiatives emphasize transparency, safety, and environmental commitment, laying a foundation of trust that supports both the public perception and practical realization of LNG projects. In conclusion, LNG represents a highly strategic, economic, and environmental asset in the global push towards more flexible, secure, and sustainable energy systems. Expert insights demonstrate that when managed prudently, LNG stands as an exemplar of modern energy solutions, promising a brighter, cleaner, and more connected energy future.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

