
2 月 . 13, 2025 02:05
Back to list
natural gas distribution station
Navigating the world of natural gas distribution stations requires a nuanced understanding of both the operational intricacies and the broader industry implications. As an integral component of the energy infrastructure, natural gas distribution stations serve as crucial nodes that ensure the safe and efficient delivery of natural gas from producers to consumers. In order to gain a comprehensive perspective on these facilities, it is essential to explore their design, functionality, safety protocols, and regulatory frameworks while also appreciating their economic and environmental impacts.
Trustworthiness in the operations of natural gas distribution stations is built upon transparency, community engagement, and continuous improvement. Energy companies often collaborate with local governments and communities to address any concerns related to safety and environmental impacts. Public education campaigns and transparent communication channels foster trust and understanding between operators and the communities they serve. Additionally, the industry’s commitment to innovation and investment in greener technologies also underscores a dedication to sustainable practices. Product innovations related to natural gas distribution have centered around enhancing safety and efficiency. Advanced materials and construction techniques are employed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stresses. Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies—such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics—enables predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, which significantly reduce downtime and operational risks. These technological advancements facilitate the seamless distribution of natural gas, making it a more reliable energy source for millions of homes and businesses worldwide. Environmentally, natural gas distribution stations contribute to the reduction of carbon footprints when they replace more pollutant fossil fuels like coal and oil. The ability to distribute natural gas efficiently encourages broader adoption of cleaner energy sources. Moreover, the industry is actively engaged in reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, through improved equipment and leak detection technologies—an effort aligned with global sustainability goals. In conclusion, natural gas distribution stations are a vital linchpin in the global energy infrastructure, representing a blend of sophisticated engineering and rigorous safety protocols. Expertise and authoritative oversight ensure these facilities operate smoothly and safely, while trust in their operations is cultivated through transparency and community engagement. As the energy landscape evolves, distribution stations will continue to adapt, driving technological innovation and environmental stewardship to meet the demands of a sustainable future.
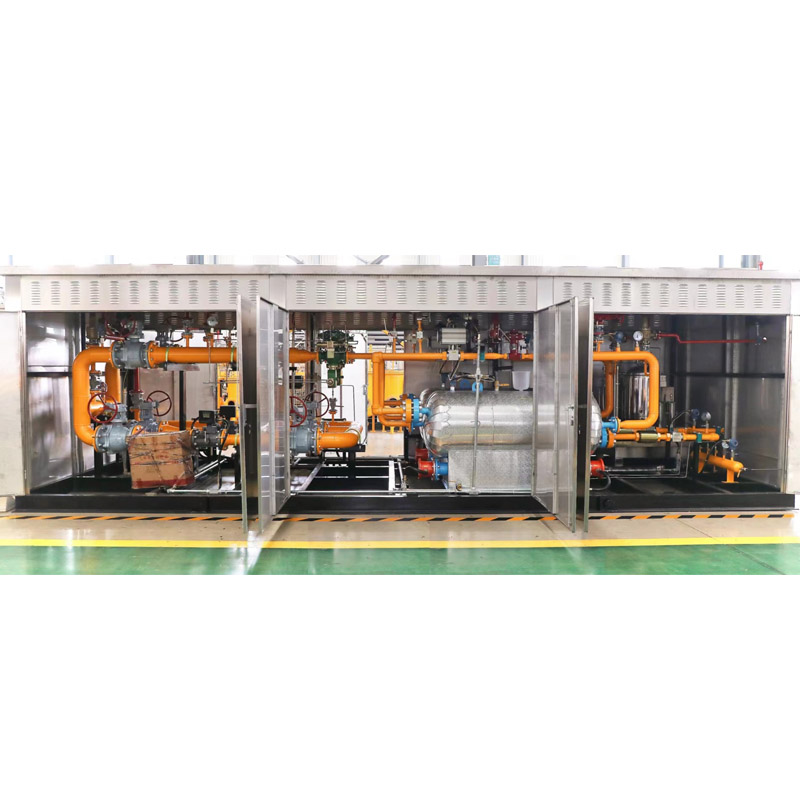

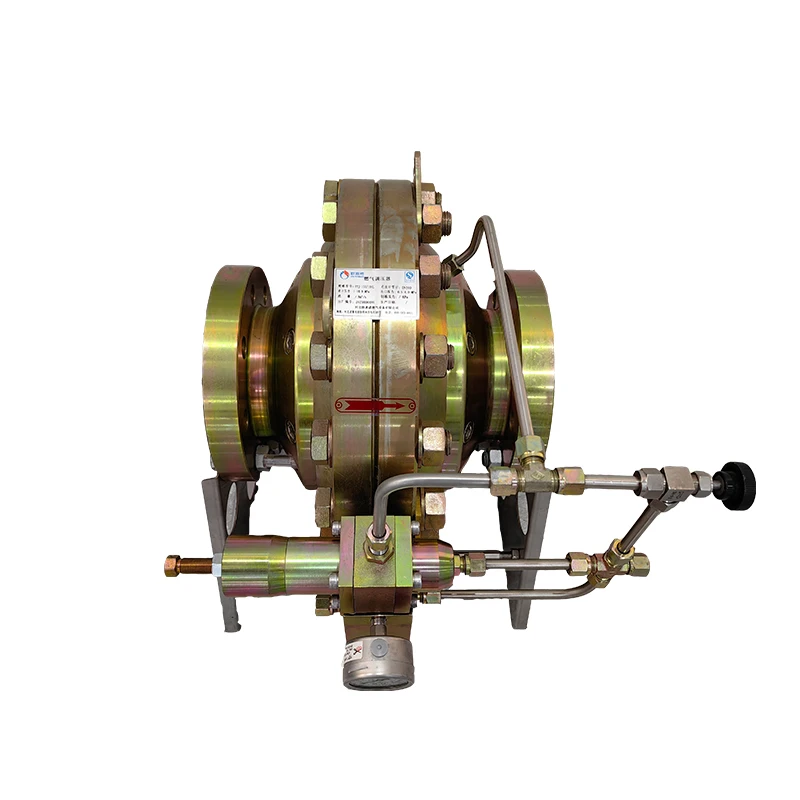
Trustworthiness in the operations of natural gas distribution stations is built upon transparency, community engagement, and continuous improvement. Energy companies often collaborate with local governments and communities to address any concerns related to safety and environmental impacts. Public education campaigns and transparent communication channels foster trust and understanding between operators and the communities they serve. Additionally, the industry’s commitment to innovation and investment in greener technologies also underscores a dedication to sustainable practices. Product innovations related to natural gas distribution have centered around enhancing safety and efficiency. Advanced materials and construction techniques are employed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stresses. Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies—such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics—enables predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, which significantly reduce downtime and operational risks. These technological advancements facilitate the seamless distribution of natural gas, making it a more reliable energy source for millions of homes and businesses worldwide. Environmentally, natural gas distribution stations contribute to the reduction of carbon footprints when they replace more pollutant fossil fuels like coal and oil. The ability to distribute natural gas efficiently encourages broader adoption of cleaner energy sources. Moreover, the industry is actively engaged in reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, through improved equipment and leak detection technologies—an effort aligned with global sustainability goals. In conclusion, natural gas distribution stations are a vital linchpin in the global energy infrastructure, representing a blend of sophisticated engineering and rigorous safety protocols. Expertise and authoritative oversight ensure these facilities operate smoothly and safely, while trust in their operations is cultivated through transparency and community engagement. As the energy landscape evolves, distribution stations will continue to adapt, driving technological innovation and environmental stewardship to meet the demands of a sustainable future.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

