
2 月 . 11, 2025 22:06
Back to list
regulating valve
In the realm of industrial automation and fluid control, the regulating valve is an indispensable component that plays a pivotal role in numerous processes across various sectors. These devices are omnipresent in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage processing. Their primary purpose is to maintain the desired flow rate, pressure, and temperature, ensuring optimal efficiency and safety of the entire system.
Diaphragm valves are ideal for handling corrosive or abrasive fluids, thanks to their simple design that minimizes the risk of fluid contamination. They are commonly used in industries requiring stringent hygiene standards, albeit their ability to handle high pressure is limited compared to other types. Incorporating a regulating valve into an industrial system significantly enhances process automation. By integrating advanced technologies such as smart sensors and feedback loops, regulating valves can automatically adjust to variations in process parameters, ensuring consistent performance. Moreover, modern digital control systems can provide real-time analytics, predictive maintenance insights, and enhanced system diagnostics. This technological evolution not only optimizes operational efficiency but also significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs. However, the successful deployment of regulating valves requires a thorough understanding of installation, maintenance, and calibration processes. Proper installation involves ensuring compatibility with existing system components, adequate support and alignment, and adherence to safety standards. Regular maintenance checks are crucial in identifying wear and tear, which could affect valve performance. Calibration, on the other hand, involves adjusting the valve to maintain accuracy in flow control parameters, which is pivotal in maintaining process efficiency. Expertise in selecting and managing these components is often backed by extensive industry experience and technical knowledge. This expertise ensures not only the selection of the most suitable valve for a given application but also its optimum integration and operation within the system. In conclusion, the regulating valve is more than just a component; it's a critical element that influences the overall effectiveness of industrial systems. By understanding its types, operational mechanisms, and integration techniques, industries can harness their full potential to achieve enhanced performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. As industrial processes continue to evolve, the role of regulating valves in ensuring seamless, automated, and efficient operations remains ever-critical. The choice and management of these valves should thus be guided by a blend of experience, technical knowledge, and a proactive approach to industry innovations.
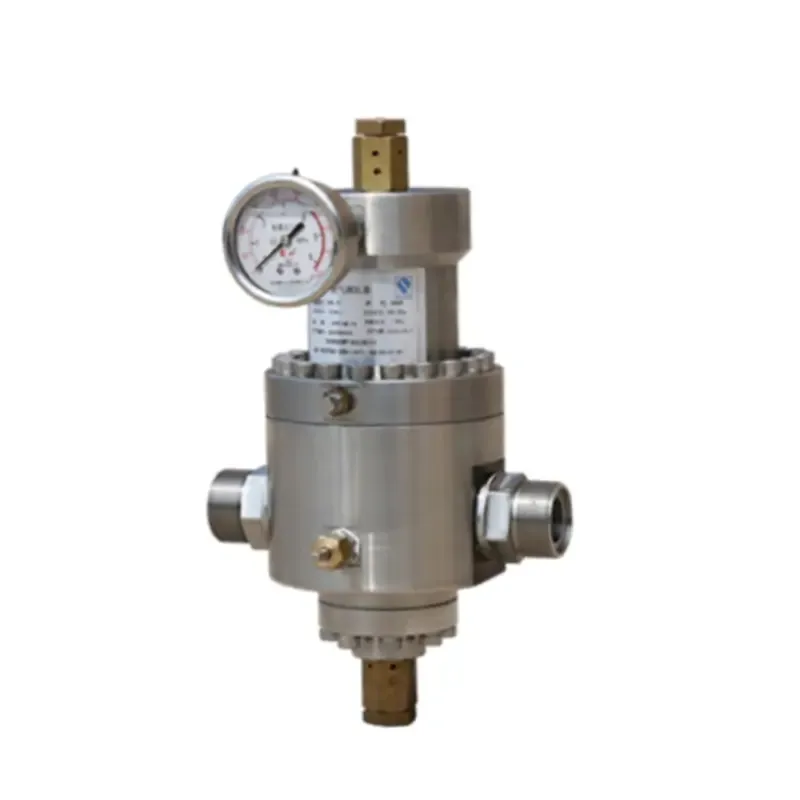

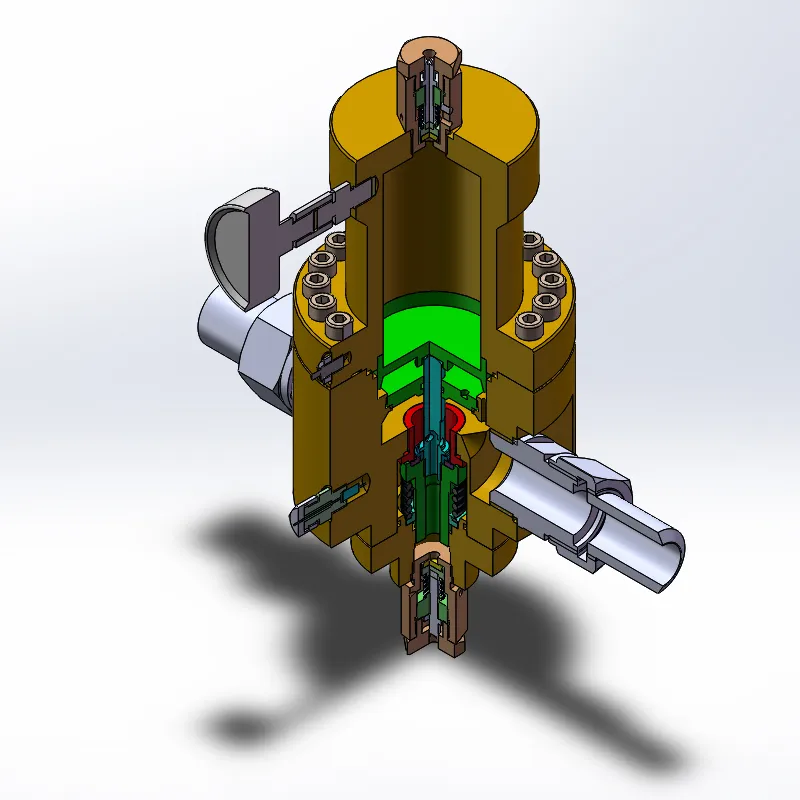
Diaphragm valves are ideal for handling corrosive or abrasive fluids, thanks to their simple design that minimizes the risk of fluid contamination. They are commonly used in industries requiring stringent hygiene standards, albeit their ability to handle high pressure is limited compared to other types. Incorporating a regulating valve into an industrial system significantly enhances process automation. By integrating advanced technologies such as smart sensors and feedback loops, regulating valves can automatically adjust to variations in process parameters, ensuring consistent performance. Moreover, modern digital control systems can provide real-time analytics, predictive maintenance insights, and enhanced system diagnostics. This technological evolution not only optimizes operational efficiency but also significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs. However, the successful deployment of regulating valves requires a thorough understanding of installation, maintenance, and calibration processes. Proper installation involves ensuring compatibility with existing system components, adequate support and alignment, and adherence to safety standards. Regular maintenance checks are crucial in identifying wear and tear, which could affect valve performance. Calibration, on the other hand, involves adjusting the valve to maintain accuracy in flow control parameters, which is pivotal in maintaining process efficiency. Expertise in selecting and managing these components is often backed by extensive industry experience and technical knowledge. This expertise ensures not only the selection of the most suitable valve for a given application but also its optimum integration and operation within the system. In conclusion, the regulating valve is more than just a component; it's a critical element that influences the overall effectiveness of industrial systems. By understanding its types, operational mechanisms, and integration techniques, industries can harness their full potential to achieve enhanced performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. As industrial processes continue to evolve, the role of regulating valves in ensuring seamless, automated, and efficient operations remains ever-critical. The choice and management of these valves should thus be guided by a blend of experience, technical knowledge, and a proactive approach to industry innovations.
Next:
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

