
2 月 . 18, 2025 04:28
Back to list
safety relief valve
Safety relief valves are critical components in a multitude of industrial applications, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of various systems. These devices serve as the last line of defense against excessive pressure build-up, preventing potential disasters in environments ranging from chemical plants to power generation facilities.
Trustworthiness is inherently linked to the reliability and quality assurance provided by manufacturers and suppliers of safety relief valves. Companies with a long track record in the industry often offer robust warranties and service agreements, affirming their commitment to delivering quality products. Customers frequently rely on trusted brands, as the consequences of valve failure can be dire. Moreover, trustworthy companies often provide comprehensive after-sales support, including maintenance services and technical training for operators, ensuring the continued effectiveness of their products. Choosing the right safety relief valve requires careful consideration of operational conditions, including the pressure and temperature range, the type of media being handled, and the installation environment. For instance, industries using corrosive media such as caustic chemicals must utilize valves made from resistant materials like stainless steel or specialized alloys to prevent premature failure. In contrast, high-temperature applications may necessitate valves made from materials capable of retaining structural integrity under extreme heat. Furthermore, the integration of digital monitoring systems with traditional safety relief valves has emerged as a modern advancement, adding an extra layer of security. These systems provide real-time data on valve performance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. This integration exemplifies the fusion of traditional engineering with cutting-edge technology to enhance safety and operational efficiency. In summary, safety relief valves are indispensable for maintaining safety and operational integrity in various industries. Experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness are paramount in ensuring that these critical components perform their intended function reliably and effectively. By staying abreast of industry standards, leveraging technological advancements, and prioritizing quality assurance, companies can significantly mitigate risks associated with pressure-related incidents.
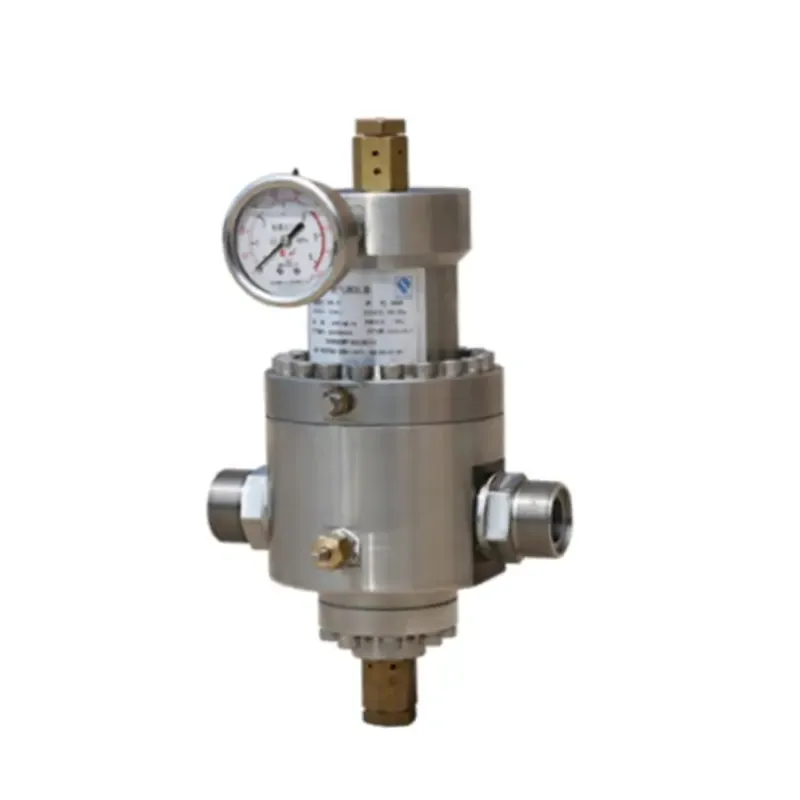
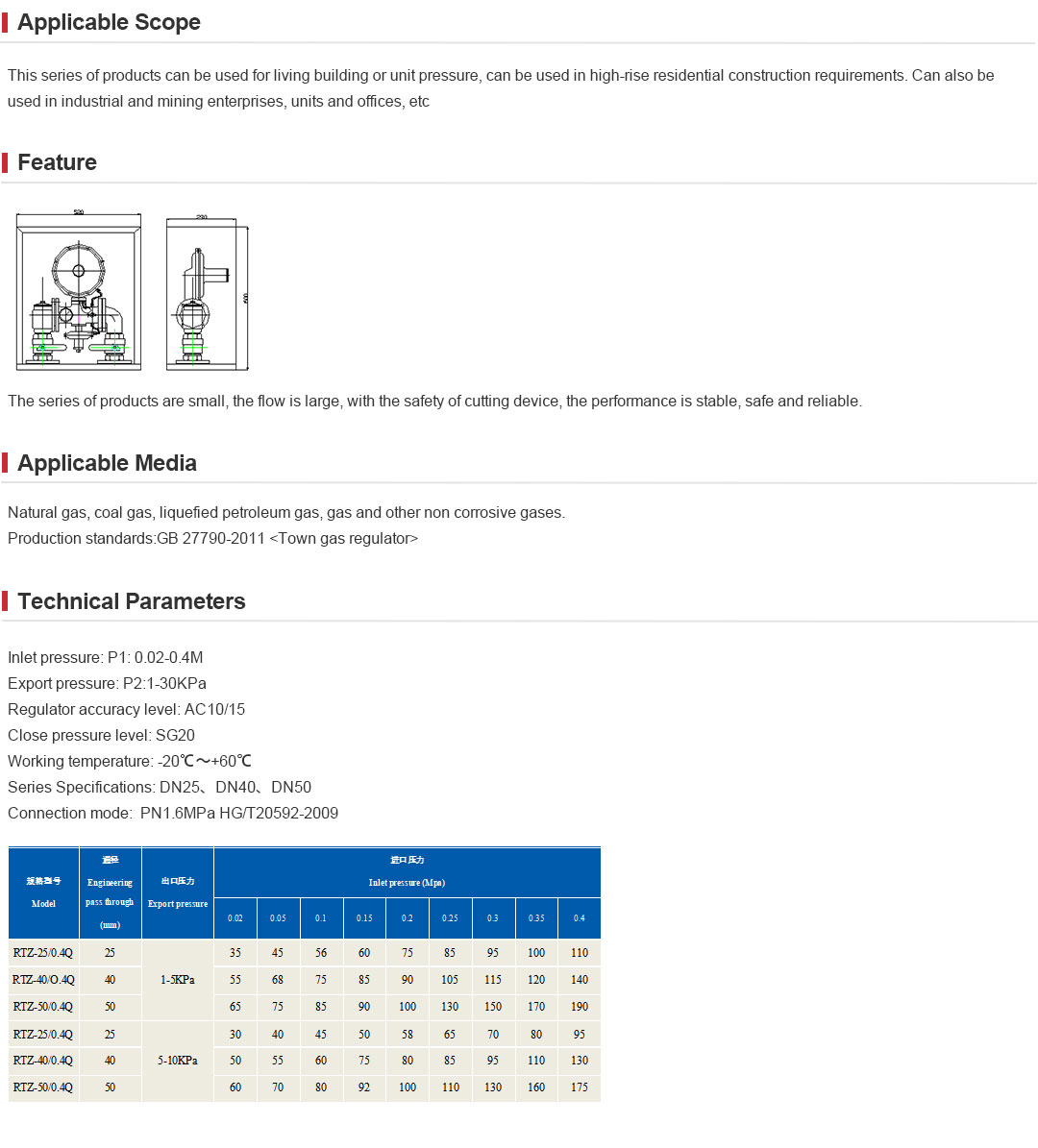

Trustworthiness is inherently linked to the reliability and quality assurance provided by manufacturers and suppliers of safety relief valves. Companies with a long track record in the industry often offer robust warranties and service agreements, affirming their commitment to delivering quality products. Customers frequently rely on trusted brands, as the consequences of valve failure can be dire. Moreover, trustworthy companies often provide comprehensive after-sales support, including maintenance services and technical training for operators, ensuring the continued effectiveness of their products. Choosing the right safety relief valve requires careful consideration of operational conditions, including the pressure and temperature range, the type of media being handled, and the installation environment. For instance, industries using corrosive media such as caustic chemicals must utilize valves made from resistant materials like stainless steel or specialized alloys to prevent premature failure. In contrast, high-temperature applications may necessitate valves made from materials capable of retaining structural integrity under extreme heat. Furthermore, the integration of digital monitoring systems with traditional safety relief valves has emerged as a modern advancement, adding an extra layer of security. These systems provide real-time data on valve performance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. This integration exemplifies the fusion of traditional engineering with cutting-edge technology to enhance safety and operational efficiency. In summary, safety relief valves are indispensable for maintaining safety and operational integrity in various industries. Experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness are paramount in ensuring that these critical components perform their intended function reliably and effectively. By staying abreast of industry standards, leveraging technological advancements, and prioritizing quality assurance, companies can significantly mitigate risks associated with pressure-related incidents.
Latest news
-
Unlocking The Quality Gas Pressure ReducersNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Role of Gas Pressure Reducing StationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Importance and Functionality of Safety Relief ValvesNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Safety Valves in Natural Gas ApplicationsNewsNov.01,2024
-
The Essential Role of Gas Pressure RegulatorsNewsNov.01,2024
-
Enhance Your Premium Gas FiltersNewsNov.01,2024

